The nephron consists of a renal corpuscle (the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule), a proximal tubule (with convoluted and straight portions), a thin segment, and a distal tubule (with straight and convoluted portions). Nestled into the vascular pole of the nephron is a collection of cells called the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA). 66 55. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the The urinary bladder, or simply bladder, is a hollow organ in humans and other vertebrates that stores urine from the kidneys before disposal by urination.In humans the bladder is a distensible organ that sits on the pelvic floor.Urine enters the bladder via the ureters and exits via the urethra.The typical adult human bladder will hold between 300 and 500 ml (10.14 and 16.91 fl oz) A blood group also called a Blood Type Classification of blood is based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs) These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system. All cells of the human body are eukaryotic, meaning that they are organized into two parts: nucleus and cytoplasm. 
 Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) Lying just outside Bowmans capsule and the glomerulus is the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) (Figure 25.2.4). Alveoli are comprised of two types of cells. The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent glomerular arteriole, the efferent glomerular arteriole, the extraglomerular mesangial cells, and that small portion of the distal tubule known as the macula densa that is located beside the renal glomerulus. The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) is an area of the nephron where the afferent arteriole and the initial portion of the distal convoluted tubule are in close contact. The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) consists of cells located in and around the glomerulus and the glomerular capsule. As a result, we can observe the fluid movement results, which can typically manifest as edema, dehydration, changes in blood pressure, seizures, and changes in intracranial
Juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) Lying just outside Bowmans capsule and the glomerulus is the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) (Figure 25.2.4). Alveoli are comprised of two types of cells. The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of the juxtaglomerular cells of the afferent glomerular arteriole, the efferent glomerular arteriole, the extraglomerular mesangial cells, and that small portion of the distal tubule known as the macula densa that is located beside the renal glomerulus. The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) is an area of the nephron where the afferent arteriole and the initial portion of the distal convoluted tubule are in close contact. The juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) consists of cells located in and around the glomerulus and the glomerular capsule. As a result, we can observe the fluid movement results, which can typically manifest as edema, dehydration, changes in blood pressure, seizures, and changes in intracranial 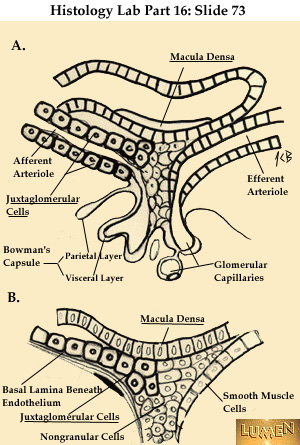 Juxtaglomeruar Apparatus (JGA) consists of: 1) Juxtaglomerular A. the juxtaglomerular cells send a message to the afferent arteriole to dilate. The cytoplasm contains specialized subunits called organelles which work like little organs. It consists of two layers (parietal and visceral), which bound a cavity called the glomerular capsular space (Bowmans / urinary space). The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of JGA secretes the enzyme renin which is mainly involved in the homeostasis of blood volume. A portal triad consists of which three elements? The juxtaglomerular apparatus. 2 The _____ of blood forces water and solutes out of the blood and into the capsule. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Juxtaglomerular apparatus or JGA is a group of specialized cells that are located in the afferent arteriole that then enters the renal corpuscle. 16/09/2015 4Mujtaba Ashraf 5. The juxtaglomerular apparatus (also known as the juxtaglomerular complex) is a structure in the kidney that regulates the function of each nephron, the functional units of the kidney.The juxtaglomerular apparatus is named because it is next to (juxta-) the glomerulus.The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of three types of cells: the macula densa, a part of the Cells and tissues A cell is the smallest functional unit of an organism. KIDNEY FUNCTIONS 56. Mitoses (6) are frequently observed in the deeper cell layers and in the basal cells (5).
Juxtaglomeruar Apparatus (JGA) consists of: 1) Juxtaglomerular A. the juxtaglomerular cells send a message to the afferent arteriole to dilate. The cytoplasm contains specialized subunits called organelles which work like little organs. It consists of two layers (parietal and visceral), which bound a cavity called the glomerular capsular space (Bowmans / urinary space). The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of JGA secretes the enzyme renin which is mainly involved in the homeostasis of blood volume. A portal triad consists of which three elements? The juxtaglomerular apparatus. 2 The _____ of blood forces water and solutes out of the blood and into the capsule. In human females and other primates, the urethra connects to the urinary meatus above the vagina, whereas in marsupials, the female's urethra empties into the urogenital sinus. Juxtaglomerular apparatus or JGA is a group of specialized cells that are located in the afferent arteriole that then enters the renal corpuscle. 16/09/2015 4Mujtaba Ashraf 5. The juxtaglomerular apparatus (also known as the juxtaglomerular complex) is a structure in the kidney that regulates the function of each nephron, the functional units of the kidney.The juxtaglomerular apparatus is named because it is next to (juxta-) the glomerulus.The juxtaglomerular apparatus consists of three types of cells: the macula densa, a part of the Cells and tissues A cell is the smallest functional unit of an organism. KIDNEY FUNCTIONS 56. Mitoses (6) are frequently observed in the deeper cell layers and in the basal cells (5).
Type _____ are thin squamous cells. Cells and their nuclei become progressively flatter as the cells migrate toward the free surface of the epithelium. JUXTAGLOMERULAR APPARATUS The distal end of the renal tubule passes next to the glomerulus to form the juxtaglomerular apparatus (juxta means next to). TOP( then go clockwise) glomerulus afferent arteriole juxtaglomerular cells Specialised cells that make up the juxtaglomerular apparatus of the kidney can sense changes in BP. 2 kidneys, 2 urethra, bladder, 1 ureter. It is divided into two subgroups, single-unit and multiunit smooth muscle. The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule.The renal tubule extends from the capsule. Smooth muscle is an involuntary non-striated muscle, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (bands or stripes). Type _____ are large cuboidal cells. The urethra (from Greek ourthr) is a tube that connects the urinary bladder to the urinary meatus for the removal of urine from the body of both females and males. Juxtaglomerular Apparatus or Complex is a specialized region of a nephron where the afferent arteriole and Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) come in direct contact with each other. Label the structures of the renal corpuscle and juxtaglomerular apparatus. 1 The renal corpuscle consists of a capillary bed called the _____ and a capsule of epithelial cells. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium.. The macula densa sends a message to the efferent arteriole to constrict. In this, the solutes and fluids are filtered out from the blood and are transferred into the Bowmans capsule. Organelles can be membranous (mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum) or non Cells in the intermediate layers of the epithelium are polyhedral (4) with round or oval nuclei, and more visible cell cytoplasm and membranes. B. A. What does the renal system consists of? The plasma osmolality and oncotic pressures in an organism can determine the direction of fluid movement within the system; therefore, the relative concentration of ions and protein in the solvent. How does the juxtaglomerular apparatus respond when systemic blood pressure is too high?
Ranges of Normal Values in Human Whole Blood (B), Plasma (P), or Serum (S)a Normal Value (Varies with Procedure Used) Determination Traditional Units SI (lacis cells) form the "juxtaglomerular apparatus".