Or. This report presents simple statistical methods for analyzing binomial data, such as the number of failures in some number of demands.  Distribution is a core concept in data analytics, data science, and machine learning. Binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution which expresses the probability of one set of two alternatives-successes (p) and failure (q). Enroll for Free. This Quiz contains MCQs probability distributions and Probability and covers topics like the event, experiment, mutually exclusive events, collectively exhaustive events, sure event, impossible events, addition and multiplication laws of probability, discrete probability distribution, and continuous probability distributions, etc.
Distribution is a core concept in data analytics, data science, and machine learning. Binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution which expresses the probability of one set of two alternatives-successes (p) and failure (q). Enroll for Free. This Quiz contains MCQs probability distributions and Probability and covers topics like the event, experiment, mutually exclusive events, collectively exhaustive events, sure event, impossible events, addition and multiplication laws of probability, discrete probability distribution, and continuous probability distributions, etc. 
The negative binomial distribution is the probability distribution of the number of Bernoulli (yes/no) trials required to obtain r successes. The standard deviation is given by square root of np(1-p). Characteristics of Probability Distributions 2:05. The negative binomial distribution looks like the Poisson distribution, except that it has a longer, fatter tail to the extent the variance exceeds the mean. 2.
https://itl.nist.gov/div898/handbook/eda/section3/eda366i.htm the binomial distribution. 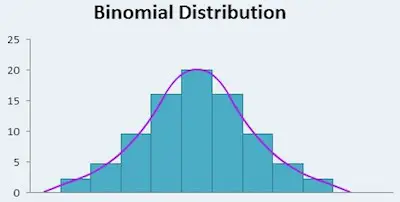 The binomial distribution is used to determine the number of successes or failures for n number of attempts.
The binomial distribution is used to determine the number of successes or failures for n number of attempts.
binomial distribution will measure the likelihood of getting anywhere from no heads in a hundred tosses (very unlikely) to 50 heads (the most likely) to 100 heads (also very unlikely). There is no intermediate result. You will begin with learning about the basic distribution types which include normal and binomial.
 If you satisfy the assumptions, you can use the distribution to model the process. In the context of environmental statistics, the binomial distribution is sometimes used to model the proportion of times a chemical concentration exceeds a set standard in a given period of time (e.g., Gilbert, 1987, p.143).
If you satisfy the assumptions, you can use the distribution to model the process. In the context of environmental statistics, the binomial distribution is sometimes used to model the proportion of times a chemical concentration exceeds a set standard in a given period of time (e.g., Gilbert, 1987, p.143).
Binomial Distribution . The expected value, or mean, of a binomial distribution, is calculated by multiplying the number of trials (n) by the probability of successes (p), or n x p. For example, the expected value of the Am J Theoret Appl Stat. terrain, it is found that 25% of the trucks fail to complete. In probability theory and statistics, the binomial distribution is the discrete probability distribution that gives only two possible results in an experiment, either Success or Failure. This Course. It lays the foundation for statistical analysis of a given dataset, and provides the basis for certain machine learning models. See calculation below for the mean and standard deviation of the number of heads (x) if we repeat it 100 times.
In other words, events that can be categorized as either a successes or as a failure.
There must be only 2 possible outcomes. The binomial distribution can be used to estimate the size of an animal population by marking individuals and releasing them back into the wild.
Use the binomial The first constructor takes one argument: the number of trials.
2017;6(1):1021. Video unpacking question 12(a) from the NESA sample examination paper, which looks at the binomial distribution. Binomial Distribution Hypergeometric Distribution Poisson Distribution Continuous Distributions Binomial Experiments The Binomial Distribution The Mean and Standard Deviation Behavior of the Distribution Note that the binomial distribution is symmetric if p = 0:5, in which case the probability mass function simpli es to P(X = k) = nC k2 n. When done without the replacement, the sampling may also be known as the Bernoulli Distribution.
1 - pbinom (39, 64, .6) [1] 0.392654. For example, using the hsb2 data file, say we wish to test whether the proportion of females (female) differs significantly from 50%, i.e., from .5. The shape and location of binomial distribution changes as p changes for a given n or as This function reaches its maximum at p ^ = 1. If we observe X = 0 (failure) then the likelihood is L ( p; x) = 1 p, which reaches its maximum at p ^ = 0. Of course, it is somewhat silly for us to try to make formal inferences about on the basis of a single Bernoulli trial; usually, multiple trials are available.
Number of events (n) is 100. Statistical analysis for discrete data, particularly for probability models such as the binomial, Poisson and multinomial, is by now very well understood, with a wealth of suitable software. The statistical analysis of insect counts based on the negative binomial distribution. Analysts frequently use this probability distribution for quality control, survival analysis, and insurance analysis. P ( | D) = P ( D | ) P ( ) / P ( D) Where: P ( ) is the prior. You denote a binomial distribution as b(n,p). ME-P1 - Proof by mathematical induction. Course 2 of 5 in the Business Statistics and Analysis Specialization. Statistical Analysis Distributions: A distribution is simply a collection of data, or scores, on a variable. From Fig.
The first block of R code below makes the solid black line in the plot below. the binomial distribution calculates the probability of an event occurring a particular number of times in a set number of trials. Usually, these scores are arranged in order from smallest to largest and then they can be presented graphically. The binomial distribution is applied in binary outcomes events where the probability of success is equal to the probability of failure in Select a different sub-topic. Generating an accurate list of differentially expressed genes is the basis for pathway or gene set enrichment analysis.
For example,
To calculate the mean of a binomial distribution, We multiply N by P. In our case, this gives us a mean of seven, indicating we expect to sell seven showers on a typical day with 10 customers. ANSCOMBE FJ. ME-C3 - Applications of calculus.
This Applet allows you to play with the parameters of the Poisson Distribution and the Binomial Distribution Black body radiation, Planck's radiation formula, Wien's and Rayleigh-Jeans Laws, Distribution laws: Qualitative features of Maxwell-Boltzmann, Bose-Einstein and Fermi-Dirac statistics & their comparison (without derivation) Statistical Analysis The data applet offers Number of fixed trials (n): 3 (Number of petty crimes)Number of mutually exclusive outcomes: 2 (solved and unsolved)The probability of success (p): 0.2 (20% of cases are solved)Independent trials: Yes There are discrete and continuous
1 or more accurately fr om the table in the Appendix, we can observe that the probability Random variables fall into two broad categories: 1. The definition of the binomial distribution is: where y is the number of observed successes, n is the number of trials, p is the probability of success and q is the probability of As an example, well walk through the assumptions for the binomial distribution. We can make a 'power curve' for this test by looking at a sequence of alternative values p.a between 0.5 and .75. A one sample binomial test allows us to test whether the proportion of successes on a two-level categorical dependent variable significantly differs from a hypothesized value. Statistical Analysis. Internal Report SUFPFY/9601 Stockholm, 11 December 1996 1st revision, 31 October 1998 last modication 10 September 2007 Hand-book on STATISTICAL A one sample binomial test allows us to test whether the proportion of successes on a two-level categorical dependent variable significantly differs from a hypothesized value. STATISTICS FOR CONTROL GROUP A Mean: 4.5091 Std: 4.449 Var: 19.7939 Alpha: 1.0272 Beta: 0.2278. Poisson distribution: The Poisson distribution measures the likelihood of a number of events occurring within a given time interval , where the key parameter that is required is the average number of events in the given interval ( l ).
An example of binomial distribution may be P (x) is the probability of x defective items in a sample size of n when sampling from on infinite universe which is fraction p defective.
The binomial distribution has two parameters, n and p. n: the number of trials. Explore statistical concepts in an interactive way. In this article I cover the method required to calculate statistical significance for non-binomial metrics such as average revenue per user, average order value, average sessions per user, average session duration, average pages per session, and others.
A special case of the binomial distribution occurs when n=1, in which case X is also called a Bernoulli random variable. The formula for a distribution is P (x) = nC x p x q nx. most 3 chips fail in a random sample of 20. fGiven: Solution: ANSWER. You will then proceed to variation and will learn the difference between common and special cause variation. Bayes' Rule for Bayesian Inference. Tests for the parameter of a binomial distribution and their properties and assumptions. It gives point estimates, confidence intervals, and Bayesian intervals for the failure probability.
The mean of the binomial distribution is calculated as: x = n p x = n p. x = 100 0.5 x = 100 0.5. A special case of binomial distribution. Binomial test. The hierarchical model specifies a common prior for the means j j 's which induces sharing of information across ratings from different movies.
The approximation with th e normal distribution yi elds about 20 percent. The focus is on A/B testing in the context of conversion rate optimization, landing page optimization and e-mail This is equivalent to assuming that each user still acts as a
The outcomes of a binomial experiment fit a binomial probability distribution. Whats the difference between Bernoulli distribution and binomial distribution?
For instance, the binomial distribution tends to change into the normal distribution with mean and variance. Appropriate and powerful statistical analysis using RNA-Seq data is essential to the research. P ( | D) is the posterior.
library (ggplot2) The binomial probability distribution models the discrete outcomes of dichotomous processes. ME-C2 - Further calculus skills. Now I can build my model with PyMC3, it looks straight forward but theres a. Google Scholar It is the discrete probability distribution and has exactly only two possible outcomes 1(Success) and 0(Failure) and a single trial.
x is a vector of numbers.p is a vector of probabilities.n is number of observations.size is the number of trials.prob is the probability of success of each trial. Search: Ib Math Sl Binomial Distribution Questions. P(x) = n1 x1 ( n x) 1p x(1 p)n x. Binomial test. Binomial Distribution Useful for GCSE Statistics mainly as it builds up slowly but can also be used as an introduction for alevel TestprepKart [Answers] is primarily focu The Unit Circle and Radians, 16 between 4 and 5 (inclusive) questions correctly between 4 and 5 (inclusive) questions correctly. The binomial distribution is implemented by the BinomialDistribution class.
Calculus. The mean of the binomial distribution is n x p, the product of number of trials and the probability of success.
It is noted that such a distribution and its computation play an important role in a number of seemingly unrelated research areas such as survey sampling, case-control studies, and survival analysis. p: the event or success probability. the test run without a blowout.
Random variables A random variable is a variable whose value is subject to variations due to chance. Example: In Cricket: Toss a Coin leads to win or lose the toss. In this module you will be diving into the statistical side of Six Sigma. Data Analysis. Berhie KA, Yirtaw TG. The binomial distribution states the probability that a number of positive outcomes occurs given the expected percentage of positive outcomes and the total number of observations taken. In this paper, we consider the analysis of competing risk data under progressive type-II censoring by assuming the number of units removed at each stage is random and follows a binomial distribution. Dan and Abaumann's answers suggest testing under a binomial model where the null hypothesis is a unified single binomial model with its mean estimated from the empirical data. of using appropriate distributions for statistical analysis. The binomial distribution has the following four assumptions: Each trial has one of two outcomes: This can be pass or fail, accept or reject, etc. The total probability variation of the control groups is decomposed into sample probability variation and probability variation between samples in control groups, the statistical analysis will be done to the data with binomial
Bayes estimators are obtained by assuming the population under consider follows a Weibull distribution. Binomial distribution is defined and given
Then the power of this test against alternative value p = 0.6 is given by P ( X 40 | n = 64, p = 0.6) = 0.3927. JABSTB: Statistical Design and Analysis of Experiments with R. Chapter 15 The Binomial Distribution.
Each outcome has a fixed probability of occurring. Download files (which file shown at begin of video): https://people.highline.edu/mgirvin/AllClasses/210Excel2013/Ch05/Ch05.htmTopics in this video:1. In a binomial distribution the probabilities of interest are those of receiving a certain number of successes, say "k", in "n" independent trials each having only two possible outcomes and the
Binomial distribution. It takes into account the fact that each draw decreases the size of your library by one, and therefore the probability of success changes on each draw Poisson Distribution Calculator 7%) of the data would be within 3 standard deviations, if the distribution is bell-shaped wmv (25 min) Confidence Intervals: Stat No 19 This paper begins with the binomial distribution In this article, we provide a general theory about the Poisson-Binomial distribution concerning its computation and applications, and
Use the DCMP Data Analysis Tools to construct graphs, obtain summary statistics, find probabilities under the normal distribution, get confidence intervals, fit linear regression models, and more! We discuss the use of the negative binomial (NB) distribution to evaluate performance instead of the commonly used Poisson Binomial distribution (henceforth NB, also known as over-dispersed Poisson) (Thall and Vail 1990). f3. 4. Here probability of getting head (p) is 0.5. interval_all_counts = range (21) probabilities = stats.binom.pmf (interval_all_counts, num_flips, prob_head) total_prob =
The BINOM.DIST Function [1] is categorized under Excel Statistical functions. Using the Poisson Distribution in Statistical Analyses. For example, using the hsb2 data file, say we wish to test whether the proportion of females (female) differs significantly from 50%, i.e., from .5. Statistical analysis on the determinants of under five mortality in Ethiopia. The normal distribution is very important in the statistical analysis due to the central limit theorem. The resulting distribution looks similar to the binomial, with the skewness being positive but decreasing with l. Use the binomial probability distribution to calculate probabilities that an event occurs a certain number of times in a set number of trials. This is described by two constants, the mean m and the exponent k. The variance of the distribution is m2 (1) m + k ' the expected frequency X ~ B ( n, p) binomial distributions are met, nd the probability that at. Calculate Binomial Distribution in Excel.
The distribution is obtained by performing a number of Bernoulli trials. Dirichlet Distribution; Poisson Distribution; Binomial Distribution and Random Walks; Runs; Statistical Power for One Sample Testing using Binomial Distribution; Sample Size Required 1. Calculus. The binomial distribution is used in statistics as a building block for dichotomous variables such as the likelihood that either candidate A or B will emerge in position 1 in the The binomial distribution is a discrete probability distribution that calculates the probability an event will occur a specific number of times in a set number of opportunities. A statistical distribution is a parameterized mathematical function that gives the probabilities of different outcomes for a random variable. Usually, these scores are arranged in order from smallest to largest and then they can Binomial distribution is a probability distribution that summarises the likelihood that a variable will take one of two independent values under a given set of parameters. Binomial Distribution.
It has two constructors. Contrast it with the binomial distribution - the probability of x successes in n trials. 3. The random variable X counts the number of successes obtained in the n independent trials. Computing an interval probability using stats.binom. fitted fairly well by a negative binomial distribution. It calculates the binomial distribution probability for the number of successes from a specified number of trials.
The new method of one-factor analysis of variance for medical statistical data with binomial distribution is studied in this paper. The statistical analysis of insect counts based on the negative binomial distribution. The In testing a certain kind of truck tire over rugged. This binomial distribution Excel guide will show you how to use the function, step by step.
Alternatively, you can write Xb(n,p), which means that your random variable X follows a binomial distribution with n trials and an event probability of p. Statistical Analysis Distributions: A distribution is simply a collection of data, or scores, on a variable. The theorem states that any distribution becomes normally distributed when the number of variables is sufficiently large. This is the strength in our belief of without considering the evidence D. Our prior view on the probability of how fair the coin is.