The epithelium of proximal convoluted tubule (PCT) of See details on the kidney and its function. The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes. You could have only 10% of your kidneys working, and you may not notice any symptoms or problems. The epithelium of The renal corpuscle consists of a network of capillaries called glomerulus and Bowman's capsule. The nephron is the main and basic structural and functional unit of kidneys. The functional units where the kidney's main functions are performed. The loss of renal function can stem from a multitude of causes that prevent normal nephron activity. Results: Each CD received CNT from 5 to 7 nephrons. It consists of a tubule which is connected with collecting duct at one end and a cup-shaped structure at the other end. Two types of nephrons. 7.4 Nephrons. Make up 85% of nephrons. 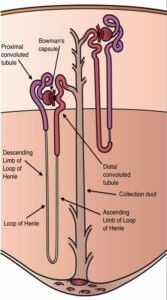 The cuboidal epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-like cells. The main function of the nephron is the filtration of blood and produce urine with the purpose of removing waste and extra fluid from the body.
The cuboidal epithelium is composed of a single layer of cube-like cells. The main function of the nephron is the filtration of blood and produce urine with the purpose of removing waste and extra fluid from the body.
Sorted by: Results 41 - 50 of 67. Diseases that reduce the number of normally functioning nephrons and/or reduce the function of nephrons cause CKD over time. Functions of a healthy kidney include maintaining a person's fluid balance, maintaining an acid-base balance; regulating electrolytes including sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearing toxins; 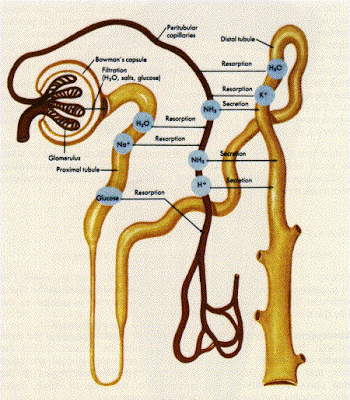 The blood entering the glomerulus is separated by space in the Bowmans capsule of two layers of cells and a basement membrane. This connective tissue is of different types as. The Bowmans capsule is a cauldron-shaped head-like structure where an intricate network of blood capillaries enter and leave. Human Excretory System functions by eliminating all the metabolic wastes from the body. Connective cells. Kidney Function and Physiology. Give Binding support. 3. Name and compare the two types of nephrons and the functional differences between them:Nephrons with a relatively short nephron loop that barely penetrate the medulla and make up the bulk of the cortex are called cortical nephrons. 2. Normal human kidneys contain about one million nephron units. The urinary system comprises of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Each kidney possesses large number of nephrons, approximately 1-1.5 million. Physicians distinguish 3 types of structural elements of the kidneys. The waste and water are excreted as urine.
The blood entering the glomerulus is separated by space in the Bowmans capsule of two layers of cells and a basement membrane. This connective tissue is of different types as. The Bowmans capsule is a cauldron-shaped head-like structure where an intricate network of blood capillaries enter and leave. Human Excretory System functions by eliminating all the metabolic wastes from the body. Connective cells. Kidney Function and Physiology. Give Binding support. 3. Name and compare the two types of nephrons and the functional differences between them:Nephrons with a relatively short nephron loop that barely penetrate the medulla and make up the bulk of the cortex are called cortical nephrons. 2. Normal human kidneys contain about one million nephron units. The urinary system comprises of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Each kidney possesses large number of nephrons, approximately 1-1.5 million. Physicians distinguish 3 types of structural elements of the kidneys. The waste and water are excreted as urine.
This is commonly found in ducts of glands and tubular parts of nephrons in kidneys and its main functions are secretion and absorption. I972.---Bird kidneys have mammaliantype (MT) as well as reptilian-type (RT) nephrons. Motor neurons transmit electrical impulses and information from the CNS to muscles in the body.
When the kidney filters are working properly, the result is a proper balance of fluids and chemicals in the body.
They are millions of tiny filtering units. Let's start with the structures of the renal corpuscle. Water potential is denoted by the Greek letter (psi) and is expressed in units of pressure (pressure is There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney. A nephron is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. Diseases that reduce the number of normally functioning nephrons and/or reduce the function of nephrons cause CKD over time. Protect. They are smaller in size with a shorter loop of Henle and penetrates less into the medulla. Different types of neurons include sensory, motor, and interneurons, as well as structurally-based neurons, which include unipolar, multipolar, bipolar, and pseudo-unipolar neurons. Muscle tissue is both extensible and elastic. Types of nephrons in kidney. Search: How To Improve Kidney Function Numbers. Blood accounts for 7% of the human body weight, with an average density around 1060 kg/m 3, very close to pure water's density of 1000 kg/m 3.  Juxtaglomerular apparatus vii. c. the loop of Henle. Rennke HG, Venkatachalam MA, Brenner BM: Hypernltration in remnant nephrons: A potentially adverse response to renal ablation (1981) by Hostetter TH, Olson JL Venue: Am J Physiol: Add To MetaCart. Nephrons are found in the kidneys. Kidney Structure. 2. The main artery is the aorta that branches into major arteries that take blood to different limbs and organs. Renal physiology (Latin rns, "kidneys") is the study of the physiology of the kidney.This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; Kidneys contain two types of nephrons, each located in different parts of the renal cortex: cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons. What is the role of the cortical vs Juxtamedullary nephrons? Start studying Renal System: Types of Nephrons. Externally, the kidneys are surrounded by three layers. Lower motor neurons: Send data from the upper motor neurons to muscles in the It is located on the right side of the abdomen. Nephrons have two lengths with different urine concentrating capacities: long juxtamedullary nephrons and short cortical nephrons. Collecting duct. Smooth muscle is found within walls of blood vessels and hollow organs such as the stomach or intestines.Cardiac muscle cells form the heart muscle, also called the false. Types of nephrons and functions. Nephron Definition. b. the proximal convoluted tubule. They function chiefly to filter blood in order to remove wastes and excess water. The uriniferous tubule (also referred as nephron) is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. What is the structure and function of nephrons? Motor neurons or motor neurons: your task is to emit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. The tissue consists of cells like fibroblasts, fat cells, macrophages, leukocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells. Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus - The Free Dictionary 13,339,950,446 visits served
Juxtaglomerular apparatus vii. c. the loop of Henle. Rennke HG, Venkatachalam MA, Brenner BM: Hypernltration in remnant nephrons: A potentially adverse response to renal ablation (1981) by Hostetter TH, Olson JL Venue: Am J Physiol: Add To MetaCart. Nephrons are found in the kidneys. Kidney Structure. 2. The main artery is the aorta that branches into major arteries that take blood to different limbs and organs. Renal physiology (Latin rns, "kidneys") is the study of the physiology of the kidney.This encompasses all functions of the kidney, including maintenance of acid-base balance; regulation of fluid balance; regulation of sodium, potassium, and other electrolytes; clearance of toxins; absorption of glucose, amino acids, and other small molecules; regulation of blood pressure; Kidneys contain two types of nephrons, each located in different parts of the renal cortex: cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons. What is the role of the cortical vs Juxtamedullary nephrons? Start studying Renal System: Types of Nephrons. Externally, the kidneys are surrounded by three layers. Lower motor neurons: Send data from the upper motor neurons to muscles in the It is located on the right side of the abdomen. Nephrons have two lengths with different urine concentrating capacities: long juxtamedullary nephrons and short cortical nephrons. Collecting duct. Smooth muscle is found within walls of blood vessels and hollow organs such as the stomach or intestines.Cardiac muscle cells form the heart muscle, also called the false. Types of nephrons and functions. Nephron Definition. b. the proximal convoluted tubule. They function chiefly to filter blood in order to remove wastes and excess water. The uriniferous tubule (also referred as nephron) is a microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney. What is the structure and function of nephrons? Motor neurons or motor neurons: your task is to emit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. The tissue consists of cells like fibroblasts, fat cells, macrophages, leukocytes, plasma cells, and mast cells. Dictionary, Encyclopedia and Thesaurus - The Free Dictionary 13,339,950,446 visits served
The nephrons remove wastes, concentrate them, and form urine that is collected in the bladder. Structure of Nephron. I972.---Bird kidneys have mammaliantype (MT) as well as reptilian-type (RT) nephrons. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreased after ca. The epithelium of MeSH. Solve any question of Excretory Products And Their Elimination with:-. They have an inherent ability to conduct an electric impulse from one region to other distant body areas. c. the loop of Henle. This classification is established according to the position of your renal corpuscles. Have short thin segments in their loop of Henle, which only penetrate a short distance into the medulla. Collecting duct. Wholekidney and individual nephron functions were studied in the desert quail during a control diuresis and during 6% NaCl infusion. Bowmans capsule iii. It is made of reticular endothelial cells. Juxtamedullary Nephrons: They form about 15 Proximal and Distal convoluted tubule iv. Types of Neurons Types of Neurons. Their function is to filter blood and produce urine. 1. The nephrons found in the Each kidney contains up to a million functioning units called nephrons. The Juxta-Medullary Nephrons These tissues are made of similar cells to have the same physiological function in the body. Considering their shapes, neurons are classified as multipolar, unipolar, and bipolar neurons. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. In the glomerulus, the blood is filtered so that a lot of water and salts flow, out of the blood, into the tubular system of the nephron. The position of renal corpuscles inside the cortex distinguishes three types of nephrons: superficial, midcortical, and juxtamedullary nephrons. Collecting duct v. Loop of Henle vi. Juxtamedullary Nephrons These are long loops of nephrons that extend to the medulla. The renal system consists of the kidney, ureters, and the urethra. There are normally approximately 700 thousand to 1 million filtering units or nephrons in each kidney. The functional units where the kidney's main functions are performed. Function of each of the parts below i. Glomerulus ii. It is made of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule. Pureblood, after the process of filtration, circulates to the other parts of the body and the waste products that get extracted pass to the ureter and enter the urinary bladder.
Each kidney consists of a cortex, medulla and calyces. The main function of the juxtamedullary nephron is to concentrate or dilute urine. By the location of renal corpuscles within the cortex, three types of nephron can be distinguished: superficial, midcortical, and juxtamedullary nephrons. These are of many types like adipose tissues, reticular tissue, etc. The Long and the Short of It: The Five Types of Bones. Juxtamedullary nephrons. Types of nephrons . Juxtamedullary nephrons- The function of the juxtamedullary nephrons is to regulate the urine concentration. Different types of nephrons. 40 mEq NaCl/ kg. The nerves send and receive signals, and act as messengers for the brain, spinal cord, and other body parts. Their main role in the body is to. The kidneys are the main organs of the urinary system. Cortical nephrons. Nerve cells, and muscle cells come under this category. Each human kidney contains about 1,200,000 nephrons, a number that does not increase after birth. It is more confined in the cortical region of the kidney. 3. Neurons are three types: sensory neurons, motor neurons and interneurons. Juxtamedullary nephron is supplied by the branches of the aorta and vena cava. The main functions of the nephron are related to filtering, reabsorbing and secreting glutamate, carbohydrates and solutes. What are the parts of a nephron and their function? The functional unit of the kidney is the nephron. Each kidney consists of millions of nephron which plays a significant role in the filtration and purification of blood. The nephron is divided into two portions, namely, the glomerulus and the renal tubule and helps in the removal of excess The mammalian nephron is a long tube-like structure, its length varying from 3555 mm long. Type 1 RTA, or distal RTA, occurs when there is a problem at the end or distal part of the tubules. Example Definitions Formulaes. In the glomerulus, the blood is filtered so that a lot of water and salts flow, out of the blood, into the tubular system of the nephron. nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney. The most primitive nephrons are found in the kidneys ( pronephros) of primitive fish, amphibian larvae, and embryos of more advanced vertebrates. Type 2 RTA, or proximal RTA, occurs when there is a problem in the beginning or proximal part of the tubules.
Tools. Each capillary is twisted into a knot called the glomerulus which is enclosed by a structure called a Bowmans capsule. Types and functions: Cortical and Juxtamedullary nephrons. Join / Login >> Class 11 >> Biology Nephrons: Structure and Types. Urea, together with water and other waste substances, forms the urine as it passes through the nephrons and down the renal tubules of the kidney. There are two types of nephrons: Cortical Nephrons These are short nephrons present in the Cortex and are high in number. Aldosterone's primary function is to act on the late distal tubule and collecting duct of nephrons in the kidney, favoring sodium and water reabsorption and potassium excretion while also contributing to acid-base What are the main parts of a nephron? Each nephron is composed of a renal corpuscle (glomerulus within Bowmans capsule), a proximal tubule (convoluted and straight components), an intermediate tubule (loop of Henle), a distal convoluted tubule, a connecting tubule, and cortical, outer medullary, and inner medullary collecting ducts. 2. There are about 1,000,000 nephrons in each human kidney. There are two kidneys, each about the size of a fist, located on either side of the spine at the lowest level of the rib cage. A nephron is the filtration unit of the kidney. Ureter There are normally approximately 700 thousand to 1 million filtering units or nephrons in each kidney. The Liver is one of the vital internal organs of the human body. First, the nephrons filter blood that runs through the capillary network in the glomerulus. Juxtamedullary nephrons are named because their loops of Henle dip all the way down to the bottom portions of the medulla. Nephrons with relatively long nephron loops that extend deep into the medulla are called juxtamedullary nephrons. The juxtamedullary nephrons concentrate or dilute urine. The two different types of nephrons and their functions are: 1. Cortical nephron is located in the cortex whereas juxtamedullary nephron is located in the medulla. The nephron, which is really a long tubule, consists of the following four parts: a. the glomerulus. Different cells carry out distinct functions in the body like. What are the functions of epithelial tissue? Nephrons take a simple blood filter and change it in urine. The kidneys are the main organs of the urinary system. The liver also performs other functions such as the manufacture of bile, which is essential for digestion. d. the distal convoluted tubule. Epithelial Tissue Function . Uriniferous tubules. Kidney nephrons. Since the nephron comprises a special collection of blood capillaries that are essential for Secretion of glutamate.
They may have longer or shorter axons, depending on how distant these neurons are from each other. Its functions include the transformation of substances that are harmful to the body into other harmless substances. It is worthwhile to describe each of them in more detail: Superficial or cortical nephron, representing the kidneys located 1 millimeter from its capsule. Which tissue in the tubular parts of nephrons provide the function of secretion and absorption ? Nephron Anatomy. In the urinary bladder, urine gets collected and is then excreted out through the urethra. These types of nephrons compose approximately 90% of human kidneys. 2. The nephron is the main functional unit of the kidney, in charge of removing metabolic waste and excess water from the blood. The nephron is the minute or microscopic structural and functional unit of the kidney.It is composed of a renal corpuscle and a renal tubule.The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and a cup-shaped structure called Bowman's capsule.The renal tubule extends from the capsule. Skeletal muscles attach to the bones of the body.Among Each nephron has a glomerulus to filter your blood and a tubule that returns needed substances to your blood and pulls out additional wastes. and air sacs of lungs and are involved in functions like forming a diffusion boundary.
There are several important cell types and three main fibers: collagen, reticular and elastic. Conductive cells. Kidneys filter blood in a three-step process. There are about a million nephrons in each kidney. At one end, the tube is closed, folded and expanded, into a double-walled, a cuplike structure called the Bowmans capsule or renal corpuscular capsule, which encloses a cluster of microscopic blood vessels called the glomerulus. The human skeleton has a number of functions, such as protection and supporting weight. Types of nephrons in human kidney. a. It helps to protect the underlying tissues from mechanical injury, entry of germs, harmful chemicals, and drying up. Nephrons are the most important part of the kidneys. There are three main types of RTA. Nephrons begin in the cortex; the tubules dip down to the medulla, then return to the cortex before draining into the collecting duct. What are the functions of epithelial tissue? Major senses such as touch and pain can Motor Neurons. The kidneys also reabsorb and return to the blood needed substances, including amino acids, sugar, sodium, potassium, and other nutrients.The kidneys filter about 200 quarts of blood per The overall function of the system filters approximately 200 liters of fluid a day from renal blood flow which allows for toxins, metabolic waste products, and excess ion to be excreted while keeping essential substances in the blood. For example, the function f (x) = Sinx, have a range [-1, 1] for the different domain values of x = n + (-1) n x. Functions of Nephron Ultrafiltration. Each kidney consists of over a million nephrons
2. Cell types based on their function. 40 mEq NaCl/ kg. It is the site of blood storage and also the destruction of worn-out red blood cells.. Thyroid Ureter The renal corpuscle consists of a tuft of capillaries called a glomerulus and an encompassing Bowmans capsule. The blood flows up to the glomerulus, encapsulated by the glomerular capsule. Nephrons - After acquiring the digitalized images and alignment, the CNT from 137 nephrons were traced with the custom-made programs. 20 mEq NaCl/kg and fell to 20% of control after cit. All the waste material sorted out from the blood in the nephrons of the kidney is passed out as urine. The renal cortex contains the nephronsthe functional unit of the kidney. How does blood enter the kidneys? A nephron consists of a renal corpuscle (glomerulus) connected to a complicated and twisted tubule that finally drains into a collecting duct (Figs. The adult human kidney contains 0.8-1.5 million nephrons, each of which constitute the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. Cortical nephrons- The function of the cortical nephrons is to regulate and excrete the waste products in the urine. Juxtamedullary nephrons are named because their loops of Henle dip all the way down to the bottom portions of the medulla. Proximal Tubule. Loop of Henle: The loop of Henle is the section of nephron lying after the proximal tubule and dips down into the renal medulla.Collecting Duct. Juxtamedullary Nephrons: Have long loops of Henle that dip far into the renal medulla. b. the proximal convoluted tubule. 2. There are two types of nephrons, according to their relative position in the cortex. Next 10 . Second, the filtrate is collected in the renal tubules. Functions and Types of Blood Vessels. 1. The corpuscle and tubule both are connected. The Superficial Nephrons Which occupies the outer two-thirds of the cortex and made up of about 85% of the total number, which is smaller and is functioning under normal conditions. Most of the macroscopic physiological function of the kidney is simply the result of the combined action of nearly a million individual nephronic units. These types of nephrons compose approximately 90% of human kidneys. Types of tissues. The juxtaglomerular apparatus is only found in juxtamedullary nephrons and not in cortical nephrons. 3. d. the distal convoluted tubule. Cortical nephrons Cortical nephrons are also known as subcapsular. Morphological Classification. Epithelial tissue covers the outside of the body and lines organs, vessels (blood and lymph), and cavities.Epithelial cells form the thin layer of cells known as the endothelium, which is contiguous with the inner tissue lining of organs such as the brain, lungs, skin, and heart.The free surface of epithelial tissue is usually exposed to fluid or The blood from the heart is carried through the body by a complex network of blood vessels. Since nephron takes care of the entire waste removal process of blood in the body and its basic Functioning of the kidney. This filtrate contains glucose, amino acids, urea, uric acid, salts and a major amount of water. Motor neurons or motor neurons: your task is to emit signals from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles. The capsule and tubule are connected and are composed of The human body is basically made of four different types of tissues. Types of Nephrons. The spleen is an organ present to the left of the stomach in the upper portion of the abdomen. There are about a million nephrons in each kidney. pressure, control levels of electrolytes. As the heart pumps the blood, the pressure of the blood pressurizes the small molecules through the capillaries to move to the capsule. Aldosterone is a mineralocorticoid hormone produced in the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex that influences water and salt regulation in the body.
It helps to protect the underlying tissues from mechanical injury, entry of germs, harmful chemicals, and drying up. Juxtamedullary Nephrons Functions of a Nephron Cortical nephron is supplied by arteries from the renal artery and veins from the renal vein. 20 mEq NaCl/kg and fell to 20% of control after cit. Nephrons. Muscle tissue. The function of nephrons in the kidney is mainly concerned with filtration, reabsorption and secretion of various solutes, carbohydrates and glutamate. The spatial arrangement of the CNT was visualized, and the length was measured. There are many different types of neurons, and they all have special functions in the brain, spinal Sensory Neurons. These Nephrons which constitute about 85% of all the Nephrons in the kidney. Macula densa viii. Its chief function is to regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances like sodium salts by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. The kidneys are paired retroperitoneal organs of the urinary system. Types of Nephrons: On the basis of location, the nephrons are of two types: 1. Reabsorbs sodium and water; Secretes potassium; These functions are regulated by ADH and aldosterone. body, regulate blood volume and. The four mechanisms used to create and process the filtrate (the result of which is to convert blood to urine) are filtration, reabsorption, secretion and excretion. A nephron is responsible for removing waste products and excess water from the blood. Internally, the kidney has three regionsan outer cortex, a medulla in the middle, and the renal pelvis, which is the expanded end of the ureter. Nephrons are two types: cortical nephrons and juxtamedullary nephrons. Glomerular filtration rate (GFR) decreased after ca. Figure 7.2 shows the structure of a single nephron.A nephron is composed of a corpuscle, located in the kidney cortex, which specializes in filtration, and a long tubule, which winds through the medulla and specializes in reabsorption and secretion. Ans: The functions of epithelial tissue are as follows: 1. A nephron is the structural and functional unit of the kidney. Nephrons eliminate wastes from the. Some acid in the blood is normal, but too much acid can disturb many bodily functions. The nephron, which is really a long tubule, consists of the following four parts: a. the glomerulus. 8. They are mainly responsible for controlling movement. To give your food a healthy boost of flavor that's packed with vitamins, use garlic instead For that, you should drink at least eight glasses of water Thankfully, with proper nutrition, kidney function can be improved urinary NGAL(Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) is a biomarker for kidney injury The normal range for males is 0 This is the most common type of neuron in the vertebrate nervous system. The kidneys also reabsorb and return to the blood needed substances, including amino acids, sugar, sodium, potassium, and other nutrients.The kidneys filter about 200 quarts of blood per Kidney nephrons. Behind the intestines are the kidneys, important organs that contain an estimated 1 million filtering units called nephrons. They may have longer or shorter axons, depending on how distant these neurons are from each other.
Wholekidney and individual nephron functions were studied in the desert quail during a control diuresis and during 6% NaCl infusion. They are responsible for removal of waste products and reabsorption of nutrient. These organs are constantly at work: Nephrons, tiny structures in the renal pyramids, filter gallons of blood each day. The force of the heart filters water and salts out of the capillaries into the tubule of the nephrons. These types of nephrons compose approximately 90% of human kidneys. Nephrons are of two types: 1. There are two main motor neurons subtypes: 4. Solve Study Textbooks Guides. ADH on the other hand enhances water reabsorption. Sensory neurons help us feel and explore the world around us.
it is responsible for making the urine diluted or concentrated. Epithelial tissue; Connective tissue; Muscular tissue; Nervous tissue. The trigonometric functions can be considered periodic functions.
The structural unit of kidneys are nephrons in which the blood gets filtered. Each nephron has a glomerulus to filter your blood and a tubule that returns needed substances to your blood and pulls out additional wastes. Blood supply. Similarly, we can write the domain and the range of the trigonometric functions and prove that the range shows up in a periodic manner. Peritubular capillaries. Classification of connective tissue into three broad types is based upon the composition of its cellular and extracellular components and its function in the body. Its main function is to regulate water and soluble substances by filtering the blood, reabsorbing water and excreting the rest as urine. Water potential can be defined as the difference in potential energy between any given water sample and pure water (at atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature). They function chiefly to filter blood in order to remove wastes and excess water. The nephron has an inflated and closed tube. Identify and describe functions of key anatomical reproductive structures present in various types of animals, including the spermatheca, the cloaca, the ovary and related structures, and the testes and related structures; Compare and contrast the process, products, and locations of male and female gametogenesis in mammals Arteries take blood away from the heart. nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. Cortical nephrons (85% of all nephrons in humans) mainly perform excretory and regulatory functions, while juxtamedullary nephrons (15% of nephrons in humans) concentrate and dilute urine. It has two types of cells: 1. Watch all CBSE Class 5 to 12 Video Lectures here. Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption and increases potassium secretion. A nephron is the kidney's filtering unit. They are mainly responsible for controlling movement. Muscular system The muscular system consists of all the body muscles. Structure of a Nephrons: Nephrons are the basic filtering units of kidneys. b. As a result of the short loop of Henle, the vasa recta of the cortical nephrons is small. Nephrons are both the structural and functional units of the kidneys. Each kidney has around a million tiny filters called nephrons. Answer: The nephrons work through a two-step process: the glomerulus filters your blood, and the tubule returns needed substances to your blood and removes wastes. Each unit has two significant parts named renal tubule and glomerulus. Aldosterone is a hormone that increases the absorption of water from the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of the kidney's nephrons. A nephron (from Greek (nephros) meaning "kidney") is the basic structural and functional unit of the kidney. The average adult has a blood volume of roughly 5 litres (11 US pt) or 1.3 gallons, which is composed of plasma and formed elements.The formed elements are the two types of blood cell or corpuscle the red blood cells, (erythrocytes) and https://www.onlinebiologynotes.com/nephron-structural-anatomy- Different types of epithelium exist throughout the nephron. These nephrons are small in number. A nephron is the basic unit of structure in the kidney.A nephron is used separate to water, ions and small molecules from the blood, filter out wastes and toxins, and return needed molecules to the blood.The nephron functions through ultrafiltration.Ultrafiltration occurs when blood pressure forces water and other small molecules through tiny gaps in The waste and water are excreted as urine. Cortical nephrons have their Loop of Henle in the renal medulla near its junction with the renal cortex, Functions of nephrons. A nephron consists of a filtering unit of tiny blood vessels called a glomerulus attached to a tubule. It branches into over 1 million capillaries inside each kidney. The kidney regulates plasma osmolarity by modulating the amount of water, solutes, The function of laci cells is unknown. Types of nephrons Nephrons are classified into three groups: juxtaglomerular, cortical, and mediocortical. The capillary network that surrounds the loop of Henle in the juxtamedullary nephrons, is called the vasa recta. nephron, functional unit of the kidney, the structure that actually produces urine in the process of removing waste and excess substances from the blood. It is the final segment of the renal tubule.